

This page will teach you about Java objects and classes. We design a
programme using objects and classes in object-oriented programming.
In Java, an object is both a physical and logical entity,
whereas a class is only a logical entity.
The classes and
objects in Java, together with their characteristics and methods,
are the foundation of OOPs. For example, a car is an
item in the actual world. The car contains characteristics like
weight and colour, as well as functions like drive,brake and
acceleration.

// Java program using class and object
class Student2{ String Stu_name ; int Stu_id; } class Student{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student2 studentObject=new Student2(); studentObject.Stu_id=40139522; studentObject.Stu_name="Dr Alok Raja"; System.out.println(studentObject.Stu_name+" \n"+studentObject.Stu_id); } }
Output:
Dr Alok Raja
40139522
We will learn how to make these objects later.
// Java program using class and object
class Student2{ String Stu_name ; int Stu_id; } class Student{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student2 studentObject=new Student2(); studentObject.Stu_id=40139522; studentObject.Stu_name="Dr Alok Raja"; System.out.println(studentObject.Stu_name+" \n"+studentObject.Stu_id); } }
Output:
Dr Alok Raja
40139522
// Java program using class and object
class Student2{ String Stu_name ; int Stu_id; public Student2(String stu_name, int stu_id) { Stu_name = stu_name; Stu_id = stu_id; } } class Student{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student2 studentObject=new Student2("Dr Alok Raja", 40139522); System.out.println(studentObject.Stu_name+" \n"+studentObject.Stu_id); } }
Output:
Dr Alok Raja
40139522
// Java program using class and object
class Student2{ String Stu_name ; int Stu_id; void insert(String stu_name, int stu_id) { Stu_name = stu_name; Stu_id = stu_id; } public void Display() { System.out.println(Stu_id); System.out.println(Stu_name+"\n"); } } class Student{ public static void main(String args[]){ Student2 studentObject1=new Student2(); Student2 studentObject2=new Student2(); studentObject1.insert("Dr Alok Raja ", 40139522); studentObject1.Display(); studentObject2.insert("Mrs Anita Sinha", 40139522); studentObject2.Display(); } }
Output:
40139522
Dr Alok Raja
40139532
Mrs Anita Sinha
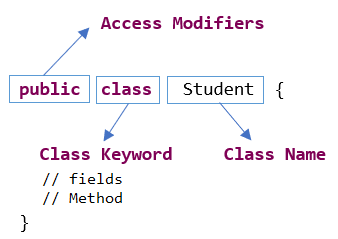
// Java program using class and object
class Car { public int gear = 2; // state public void braking() // behavior { System.out.println("Car braks Working"); } }
Post your comment